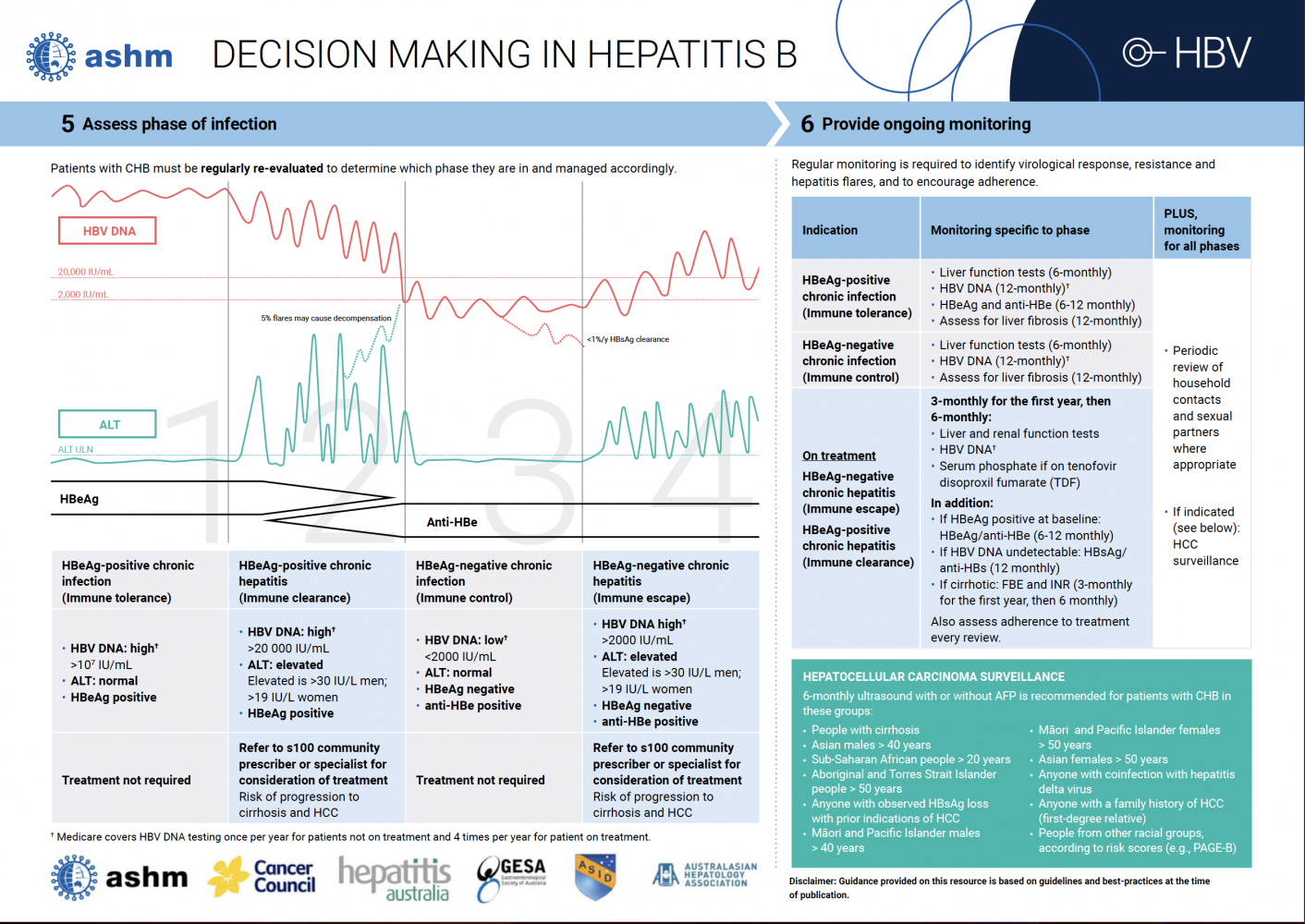
All people living with chronic HBV require at least annual monitoring to assess the phase of infection and identify if treatment is indicated.
What to do if Hepatitis B management is indicated
- Confirm the patient’s hepatitis B status
- Confirm that hepatitis B management is not being undertaken elsewhere
- Follow the ashm guidance for decision-making in HBV OR
- Refer to the guidance in:
- HealthPathways Gippsland (for clinics in Gippsland PHN)
- HealthPathways Melbourne (for clinics in Eastern Melbourne PHN and North Western Melbourne PHN)
Summary of testing for hepatitis B management
For baseline screening to assess disease phase, order:
- HBeAg and anti-HBe (hepatitis B e antigen and hepatitis B e antibody)
- HBV DNA (quantitative)*
- Full blood count
- LFT, INR and alpha fetoprotein (AFP)
- Liver ultrasound
* HBV DNA testing is Medicare rebatable once every 12 months for people not undergoing HBV treatment
Also assess for fibrosis through APRI or a FibroScan® and consider patient eligibility for HCC surveillance (AFP and liver ultrasound every 6 months)
Test for anti-HAV (Hepatitis A immunity) and coinfection with Hepatitis C, Hepatitis D and HIV if there is no previous record of testing
The screening recommendations above are dervied from the ashm guidance for decision-making in HBV, which should be referred to for detail on the assessment and monitoring of people living with chronic hepatitis B.


The HepLOGIC WALRUS risk tool
The information on this page supports the use of the POLAR/WALRUS viral hepatitis risk tool that is being tested in the HepLOGIC pilot and feasibility study. WALRUS provides an alert when a patient may be living with chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection and further assessment or management is indicated.
The hepatitis B management alert in WALRUS is triggered by ANY of the following in a patient record:
- A hepatitis B diagnosis
- A positive hepatitis B surface antigen result
- HBV DNA viral load testing ever having been ordered
- Hepatitis B management serology ever having been ordered
- Hepatitis D serology having ever being ordered (only undertaken for people living with hepatitis B)
AND the person has not had hepatitis B viral load testing ordered in the past 18 months.
The HBV viral load test (DNA test) is used as the basic indicator that hepatitis B monitoring is being undertaken, noting that other monitoring is recommended depending on the infection phase the person is currently in. HBV viral load testing is only rebatable through Medicare once every 12 months. A period of 18 months has been used as the trigger for the HepLOGIC tool to ensure that patients due not inadvertently incur a fee for testing.
Refer to ashm's quick reference guide Decision-making in HBV for best practice guidance on management.